When people talk about “the market,” they’re often referring to a single, powerful index: the S&P 500. But what exactly is the S&P 500? Why is it such a central figure in the world of investing? And in an increasingly global economy, is it still one of the smartest places to put your money?
In this post, we’ll explore what the S&P 500 is, why it remains essential, how you can invest in it, how it compares to international counterparts, and what the future may hold for this iconic index.
What Is the S&P 500?
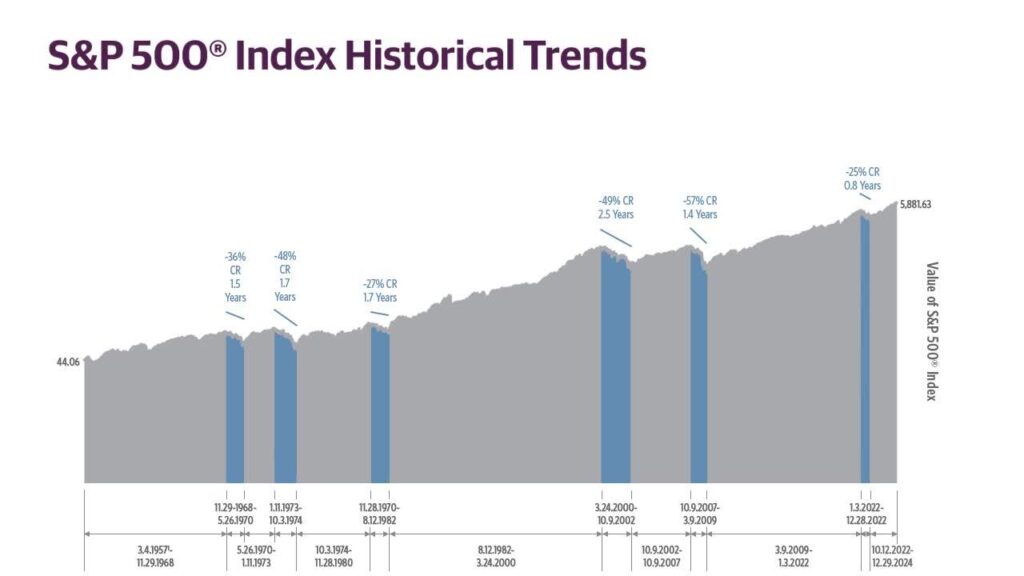
The S&P 500 (Standard & Poor’s 500 Index) is a stock market index that measures the performance of 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States. It is maintained by S&P Dow Jones Indices and includes firms across a wide array of industries.
These companies span across 11 sectors, such as:
- Information Technology (Apple, Microsoft, Nvidia)
- Health Care (UnitedHealth Group, Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson)
- Financials (JPMorgan Chase, Goldman Sachs, Bank of America)
- Consumer Discretionary (Amazon, Tesla, Nike)
- Industrials, Energy, Utilities, and others
Because of its size and diversity, the S&P 500 is often considered a mirror of the overall U.S. economy and a global benchmark for financial markets.
Why the S&P 500 Matters to Investors
Diversification with One Investment
When you invest in an S&P 500 index fund, you gain exposure to 500 different companies across multiple sectors. This gives you instant diversification, reducing the risk of investing in a single stock or sector.
Proven Long-Term Growth
Historically, the S&P 500 has delivered an average annual return of around 10% over the long term, including both bull and bear markets. While no returns are guaranteed, it’s one of the most consistent performers over time.
High Liquidity and Institutional Trust
The S&P 500 is widely used by institutional investors—such as pension funds and hedge funds—as a benchmark. Its size and visibility ensure high liquidity, making it easy to buy and sell with minimal friction.
A Foundation of Passive Investing
With the rise of low-cost index funds and ETFs, the S&P 500 has become a cornerstone of passive investing strategies for millions of people worldwide.
How to Invest in the S&P 500
You can’t purchase the S&P 500 itself, but you can invest in funds that replicate its performance.
Top ETFs That Track the S&P 500
Here are three of the most popular exchange-traded funds that mirror the S&P 500:
- SPY (SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust) – One of the oldest and most traded ETFs.
- VOO (Vanguard S&P 500 ETF) – Known for its ultra-low expense ratio.
- IVV (iShares Core S&P 500 ETF) – A BlackRock product with strong institutional support.
Each of these funds holds the same 500 companies as the index, in nearly identical proportions. They offer:
- Low fees
- High liquidity
- Full exposure to the U.S. stock market’s blue-chip companies
These ETFs are available through most online brokers, retirement accounts, or even robo-advisors.
S&P 500 Equivalents Around the World
As investing becomes more global, it’s worth comparing the S&P 500 to its international counterparts. While it remains the most influential index globally, other markets have their own flagship indices.
🇨🇳 China: CSI 300 Index
The CSI 300 tracks 300 of the top-performing A-share stocks on the Shanghai and Shenzhen stock exchanges. It covers various sectors, with heavy representation in financials, consumer goods, and industrials.
An accessible way to invest in the CSI 300 for international investors is through the ASHR ETF (Xtrackers Harvest CSI 300 China A-Shares ETF).
🇪🇺 Europe: EURO STOXX 50
The EURO STOXX 50 represents 50 blue-chip companies from 11 countries in the Eurozone, including firms from France, Germany, Spain, and the Netherlands. Key sectors include automotive, financials, and energy.
Investors can gain exposure through the FEZ ETF (SPDR EURO STOXX 50 ETF).
🇯🇵 Japan: Nikkei 225
The Nikkei 225 includes 225 leading companies traded on the Tokyo Stock Exchange. Japan’s tech giants, automotive powerhouses, and consumer brands dominate this index.
A popular international ETF is the EWJ ETF (iShares MSCI Japan ETF), which includes major Japanese firms, although it’s not a direct replica of the Nikkei 225.
How the S&P 500 Compares to Global Indices
While all these indices serve as economic indicators in their respective regions, the S&P 500 stands out due to its strong tech sector, globalized business exposure, and market capitalization weight.
- The S&P 500 is more heavily weighted toward technology and growth companies, such as Apple, Microsoft, and Google.
- The CSI 300 leans more toward financials and state-owned enterprises.
- The EURO STOXX 50 includes more legacy industrial firms and energy companies.
- The Nikkei 225 has a strong focus on electronics, automobiles, and manufacturing.
The S&P 500’s dominance in global portfolios is also due to the strength of the U.S. dollar, the transparency of U.S. markets, and the innovative nature of its companies.
The Future of the S&P 500
The investment landscape is always changing, but the S&P 500 has shown remarkable resilience. Here’s what may shape its future:
Innovation-Led Growth
As industries like artificial intelligence, biotechnology, green energy, and digital finance evolve, new companies will rise through the ranks of the S&P 500, potentially displacing older giants.
Global Revenue Streams
While the S&P 500 consists of U.S.-listed companies, many derive a significant portion of their revenue from outside the United States. This gives investors indirect global exposure.
Regulatory and Economic Challenges
Despite its strength, the index may face headwinds from interest rate fluctuations, geopolitical tensions, tax reforms, or anti-trust regulations aimed at big tech companies.
Continued Popularity in Passive Investing
As passive investing continues to dominate, funds tracking the S&P 500 are likely to see consistent inflows, which in turn reinforces the index’s central role in the financial world.
Should You Invest in the S&P 500?
If you’re looking for:
- Long-term capital growth
- Simplicity and diversification
- Proven performance over time
Then the S&P 500 is likely a strong fit. Whether you’re investing through a retirement plan, brokerage account, or ETF portfolio, this index offers a balanced approach to equity exposure with minimal maintenance.
However, don’t forget to consider international diversification by exploring global indices like the CSI 300, EURO STOXX 50, or Nikkei 225, especially as economic growth continues to shift beyond U.S. borders.
Conclusion: The S&P 500 Remains a Pillar of Smart Investing
The S&P 500 is more than just a stock index—it’s a snapshot of corporate America, a tool for global investors, and a vehicle for long-term wealth creation. As markets change and new industries emerge, the index continues to evolve, staying relevant in a rapidly transforming world.
By understanding what the S&P 500 is, how to invest in it, and how it compares globally, you empower yourself to make smarter, more informed decisions—regardless of your experience level.
Leave a Reply