Just a decade ago, the term “real estate” conjured images of high-rise office buildings, bustling malls, cozy suburban homes, or swanky apartments in the city center. But in today’s hyper-connected world, a new type of property is quietly becoming one of the most lucrative and strategic real estate investments of our time: data centers.
Welcome to the era of digital real estate—where the infrastructure that powers our digital lives is becoming as valuable as prime physical locations.
In this post, we’ll dive deep into what data centers are, why they matter, and how savvy investors are capitalizing on this booming sector.
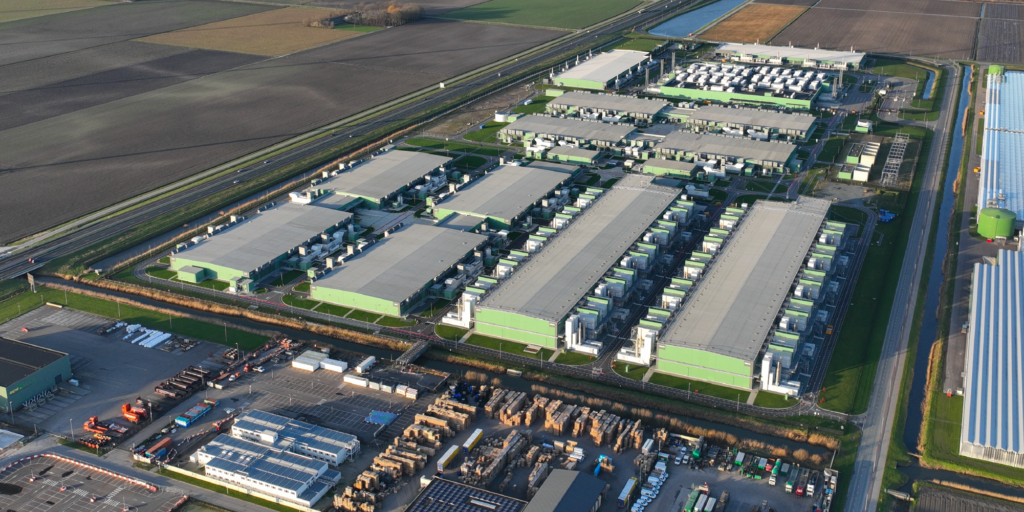

What Exactly Is a Data Center?
At its core, a data center is a highly secure facility designed to house computer systems, servers, networking equipment, and data storage. Think of it as the physical brain behind everything digital. Whether you’re scrolling through Instagram, streaming a movie on Netflix, making a bank transfer, or using artificial intelligence tools like ChatGPT—there’s a data center somewhere processing that request.
These centers are purpose-built to ensure:
- Uninterrupted power
- Advanced cooling systems to prevent overheating
- Top-tier cybersecurity protocols
- High-speed connectivity
Data centers can range from small “edge” locations in cities to massive campuses spanning hundreds of acres in rural or industrial zones.
Why Data Centers Are the Hottest New Real Estate Investment
As traditional retail and office properties face uncertainty in a post-pandemic world, data centers are soaring. Here’s why:
1. Unprecedented Demand for Data
Every day, we generate 328.77 million terabytes of data. From smart homes and autonomous vehicles to cloud computing and AI, our dependency on data is exploding. According to IDC, the world’s data is expected to grow to 175 zettabytes by 2025.
More data = more storage = more demand for data centers.
2. Digital Transformation Is Here to Stay
Remote work, e-commerce, telemedicine, fintech, and streaming services are not short-term trends. They are foundational shifts. This digital transformation requires robust infrastructure—cloud services, edge computing, AI processing—all housed in data centers.
3. Mission-Critical Infrastructure
Unlike traditional office spaces or retail shops, which can go out of fashion or sit vacant, data centers are mission-critical. Once a company signs a contract, they’re unlikely to leave. These are long-term leases with high credit tenants like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and Netflix.
From Bricks to Bits: The Shift in Real Estate Investing
Traditionally, real estate investors focused on location, location, location. But in the data center world, the equation is different. Instead of proximity to foot traffic or schools, data centers prioritize:
- Access to energy (especially renewable energy)
- Fiber connectivity and low latency networks
- Safe zones away from natural disasters
- Proximity to urban centers for edge computing needs
This shift requires investors to think beyond the physical footprint and consider the digital footprint—the unseen but essential web of infrastructure that keeps modern society functioning.
How to Invest in Data Center Real Estate
You don’t need to be a tech mogul to invest in data centers. Here are the most common ways investors are getting in:
1. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
REITs are one of the easiest ways to gain exposure. Here are some top players:
- Equinix (EQIX): The largest global data center REIT, operating over 240 centers.
- Digital Realty (DLR): Owns and operates 300+ data centers worldwide.
- CoreSite (acquired by American Tower): Focuses on interconnection and cloud access.
These companies pay dividends and offer the benefits of traditional REITs—but with the high-growth trajectory of tech.
2. Private Equity and Infrastructure Funds
Large institutional investors, including pension funds and sovereign wealth funds, are allocating billions into digital infrastructure. If you’re an accredited investor, private funds focused on data centers can offer strong returns.
3. Direct Development or Conversion Projects
Some visionary real estate developers are converting old warehouses, shopping centers, or even decommissioned industrial plants into data centers. However, this path requires deep technical partnerships, high capital, and a strong understanding of zoning, energy access, and compliance.
4. Partnering with Tech Companies
In certain cases, real estate developers partner directly with hyperscalers like Amazon, Google, or Meta to provide built-to-suit data center campuses.
The Economics of a Data Center
Here’s why investors love the numbers behind data centers:
- High Capital Costs but Predictable Returns: Data centers are expensive to build—costing $7 million to $12 million per megawatt—but leases are long-term and revenue is stable.
- Tenant Stickiness: Once in, companies don’t move. Migration of data is costly, risky, and time-consuming.
- Power = Profit: Operators often charge based on energy usage, creating scalable income streams.
- Land Appreciation: As demand grows, land suitable for data centers is rising in value, especially near fiber lines and power grids.
Global Hotspots: Where the Data Center Boom Is Happening
United States:
- Northern Virginia (Ashburn) is dubbed the “Data Center Capital of the World”
- Silicon Valley, Dallas, and Phoenix are growing rapidly
Europe:
- Frankfurt, London, Amsterdam, Paris, and Dublin (known as FLAP-D) are key markets
- Spain, Italy, and Portugal are emerging due to lower energy costs and improved connectivity
Asia-Pacific:
- Singapore, Tokyo, Hong Kong, and Sydney are leading
- India and Southeast Asia are catching up quickly
Africa & Latin America:
- Rapid growth due to mobile-first economies and expanding cloud infrastructure
Challenges and Risks
While the opportunity is huge, this sector isn’t without challenges:
- Energy Consumption: Data centers consume 1-2% of global electricity. Sustainable energy sourcing is becoming mandatory.
- Cooling Technology: As servers generate immense heat, innovations in cooling (like underwater data centers or liquid cooling) are essential.
- Regulation: Zoning laws, data sovereignty, and environmental concerns can complicate development.
- Security: Both physical and cyber security are critical—and breaches can be catastrophic.
Future Trends to Watch
1. Edge Computing
As 5G and IoT grow, there will be demand for smaller data centers closer to end-users—called edge data centers. This could decentralize data center development, opening up new investment areas.
2. Sustainable Data Centers
Net-zero carbon data centers will be the gold standard. Watch for investments in renewable-powered or green-certified facilities.
3. AI and High-Density Computing
Artificial intelligence needs enormous computing power. This means more demand for high-density racks, GPUs, and specialized infrastructure.
4. Modular and Micro Data Centers
Think shipping container-sized data centers that can be deployed anywhere. These units reduce construction time and can be moved as needed.
Why You Should Pay Attention
We often think of digital transformation in terms of apps, services, and platforms. But behind every click, swipe, and stream lies a physical foundation—one built not with bricks and mortar, but with servers and fiber.
Real estate has always been about betting on the future. Data centers are the infrastructure of that future.
If you’re a long-term investor looking for resilient income, scalable growth, and exposure to the backbone of the digital economy—data centers are no longer a niche play. They’re a necessity.
Conclusion: Real Estate Is Evolving. Are You?
The real estate of tomorrow doesn’t just house people or products—it houses data. And in an age where data is more valuable than oil, that makes data centers the next frontier for real estate investors.
Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting your journey, understanding and integrating data center assets into your strategy might be the smartest move you make in the 2020s.
Leave a Reply