The beauty industry has long been a cornerstone of global consumer spending, but few segments are growing as rapidly — and as lucratively — as the human hair extensions market. What might seem like a niche vanity product is, in reality, a billion-dollar global business with complex supply chains, high margins, and increasing demand across continents. For finance professionals, entrepreneurs, and investors, understanding where human hair comes from, how it’s traded, and what services surround it can reveal a surprisingly resilient and profitable market.

Understanding the Global Human Hair Market
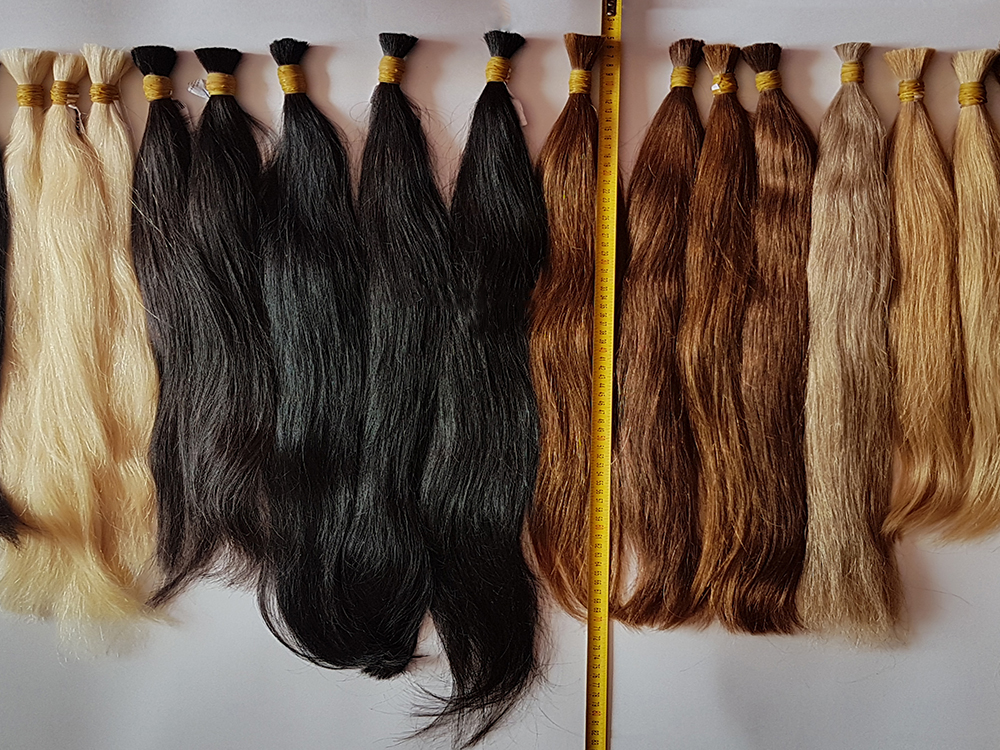
Human hair extensions are used to add length, volume, texture, and even color to natural hair. Unlike synthetic options, real human hair offers superior quality, styling versatility, and longevity. This preference for authenticity fuels a vast and growing market that spans from rural collection points in Asia and South America to high-end salons in New York, Paris, and Dubai.
According to recent industry reports, the global hair wigs and extensions market was valued at over USD 6 billion in 2023, and it’s expected to surpass USD 10 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of over 7%. A significant share of this demand is driven by female consumers seeking aesthetic enhancement, convenience, and solutions to hair loss conditions.
Where Does Human Hair Come From?
One of the most fascinating — and often misunderstood — aspects of the hair industry is its supply chain. The majority of high-quality human hair used in extensions comes from Asia and South America, particularly:
1. India and China
India is one of the largest exporters of human hair globally. Much of this comes from religious temples, especially in South India, where devotees donate their hair as an offering. This “temple hair” is highly valued for its quality and consistency.
In China, hair is often sourced from rural areas and processed in large-scale factories that specialize in cleaning, sorting, and treating the strands before export. However, the increasing global demand has led to more synthetic blends being passed off as real hair, making authentic sourcing and transparency essential in the supply chain.
2. Brazil and Peru
In South America, particularly the southern regions of Brazil and parts of Peru, local women sell their long, untreated hair, often referred to as “Virgin Brazilian Hair” — a marketing term that has gained popularity worldwide. This type of hair is prized for its thickness, durability, and natural wave.
These countries provide ethically sourced, unprocessed hair that is sought after by premium brands and salons. Entrepreneurs and traders often buy directly from individuals or small rural collection centers.
How Hair Extensions Are Sold
Hair extensions are sold through various channels, each offering unique value propositions and pricing models:
1. Wholesale Distributors
Bulk hair is often sold by weight (in grams or bundles) to salons, online retailers, or independent stylists. Wholesale prices can vary dramatically based on hair type (virgin, Remy, non-Remy), length, and origin.
2. Retail and E-commerce
The direct-to-consumer (DTC) model is booming, with online brands offering clip-ins, tape-ins, sew-ins, and wigs. Shopify stores, Amazon sellers, and beauty e-tailers have made it easier for consumers to access premium hair products globally. Retail prices can mark up 300–500% over wholesale costs.
3. Salons and Beauty Boutiques
High-end salons offer hair extensions as part of an exclusive service package. In this model, the cost includes the hair, the installation service, and often, maintenance. This vertical integration allows salons to maximize profit margins.
Related Services and Recurring Revenue Streams
Hair extensions aren’t just about the initial sale. A wide range of services and recurring revenue streams make this industry particularly attractive for business-minded investors:
- Installation Services: Professional application of extensions, ranging from sew-ins and glue-ins to micro-beads and keratin bonds. This service can cost anywhere from $100 to over $1,000 depending on the method and stylist.
- Maintenance & Styling: Regular salon visits are necessary to maintain the appearance and health of the extensions. These recurring services create consistent cash flow.
- Washing & Treatment Products: Specialized shampoos, conditioners, and serums help protect the extensions. Many brands offer private-label product lines for added revenue.
- Online Courses and Certifications: As demand grows, so does the interest in professional training. Offering certified courses in hair extension installation is a growing niche, particularly for beauty schools and online educators.
- Subscription Models: Some companies are innovating by offering monthly hair boxes or extension refresh services, helping them build brand loyalty and recurring income.
Why the Hair Extensions Industry Is Lucrative
From a financial perspective, the human hair extensions industry has many characteristics that make it highly attractive:
- High Markups: Wholesale-to-retail markups can exceed 300%, especially for virgin and Remy hair.
- Global Demand: The market isn’t limited to a region or ethnicity. Women of all backgrounds use extensions for beauty, convenience, or medical reasons.
- Recurring Services: Unlike one-time purchases, extensions require ongoing maintenance, offering steady revenue for service providers.
- Low Entry Barrier: Entrepreneurs can start small — even from home — with online sales or mobile services, then scale over time.
- Branding Opportunities: Consumers are loyal to quality and brand trust. Building a recognizable, ethical brand can command premium pricing.
In addition, the growing popularity of social media influencers, reality TV stars, and celebrity stylists has propelled demand for high-end hair products. Instagram and TikTok have become vital platforms for brand exposure, tutorials, and product placements, opening new low-cost marketing channels.
Ethical Considerations and Market Shifts
As with many lucrative markets, there are ethical questions tied to sourcing. Consumers and regulators are becoming more conscious of human rights and fair trade practices. This has created a shift toward transparency and traceability, rewarding businesses that adopt ethical sourcing models.
Eco-conscious extensions and cruelty-free certifications are gaining momentum, particularly in European and North American markets. Entrepreneurs who prioritize sustainability and social responsibility may find a competitive edge and consumer trust.
Final Thoughts: A Business with Hair-Raising Potential
What was once considered a vanity niche is now a global, multi-billion-dollar industry with opportunities across the value chain — from sourcing and manufacturing to sales, services, and education. For investors and entrepreneurs alike, the human hair extensions industry offers a blend of high margins, global scalability, and evolving consumer demand.
Whether you’re exploring a side hustle in e-commerce, thinking of launching a private-label beauty brand, or simply looking to understand emerging industries, the hair extensions market deserves serious attention.
Leave a Reply